Plumbing and Appliances:
Scale Buildup: Hard water contains high levels of calcium and magnesium, which can form scale deposits in pipes, water heaters, and appliances. This buildup can reduce water flow, decrease efficiency, and increase the risk of costly repairs.
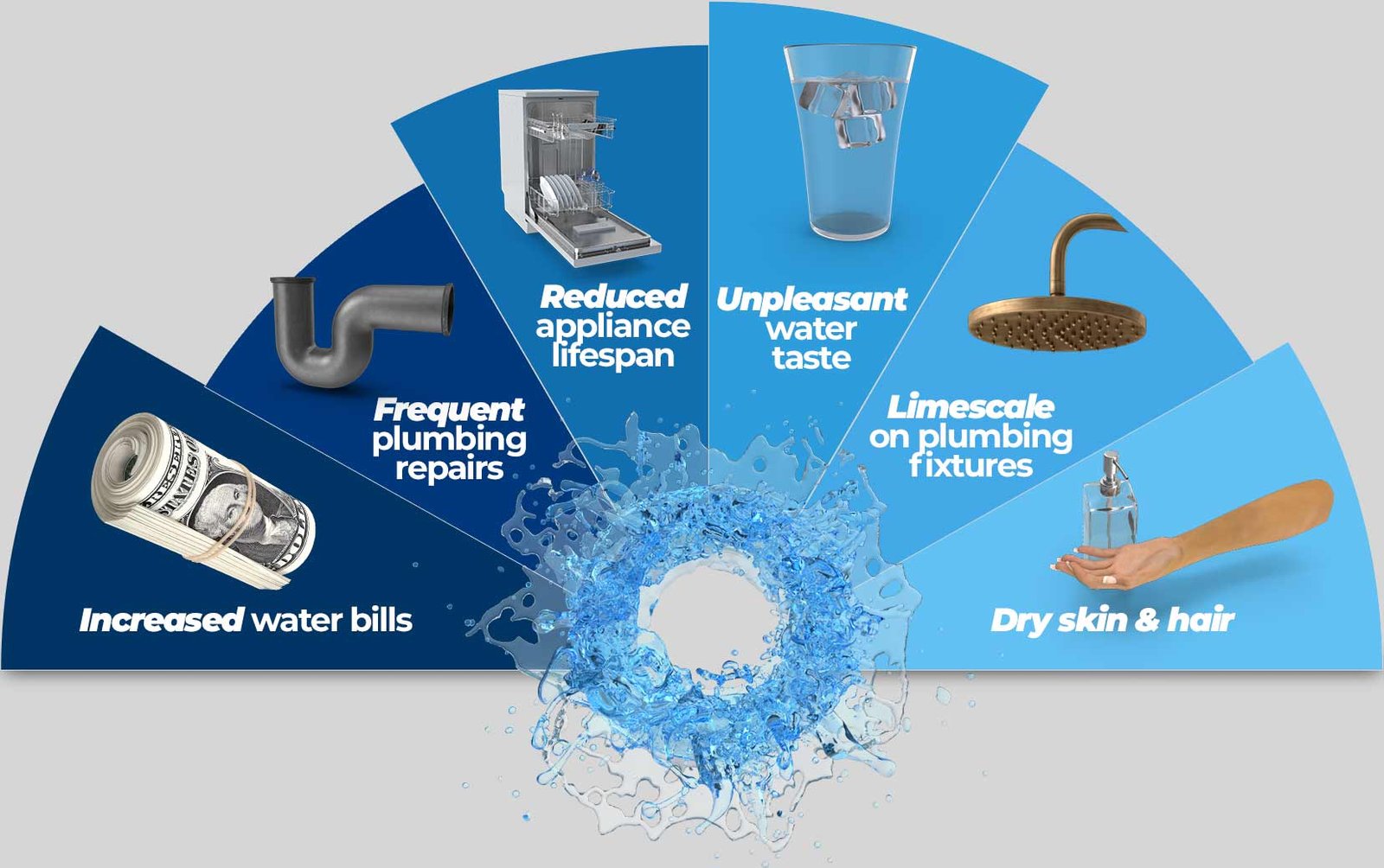
Reduced Lifespan: Appliances such as dishwashers, washing machines, and water heaters may wear out faster due to the accumulation of scale, leading to more frequent replacements.
Cleaning and Laundry:
Soap Efficiency: Hard water reduces the effectiveness of soap and detergents, making it harder to achieve a good lather. This results in using more soap and still having less effective cleaning.
Residue and Stains: Hard water can leave soap scum on dishes, glassware, and bathroom fixtures. Laundry washed in hard water may feel stiff and look dull, with potential mineral deposits left on clothes.
Increased Effort: More time and effort are needed for cleaning tasks, such as scrubbing soap scum from bathtubs and sinks.
Personal Care:
Skin and Hair Issues: Hard water can cause dry, itchy skin and dull, lifeless hair. The minerals in hard water can strip natural oils from the skin and hair, leading to dryness and irritation.
Soap Residue: Soap may not rinse off completely, leaving a residue on the skin that can clog pores and lead to acne or other skin problems.
Energy Efficiency:
Increased Energy Use: Scale buildup in water heaters and boilers can act as an insulating layer, reducing efficiency and requiring more energy to heat water. This can lead to higher utility bills.
Overall Home Maintenance:
Frequent Repairs: Appliances and fixtures may need more frequent repairs due to the damage caused by scale buildup.
Esthetic Issues: Hard water can leave mineral spots on glassware and fixtures, diminishing their appearance.
By understanding these sources, you can better address and manage hard water problems in your home.
Natural Mineral Deposits:
Groundwater: Hard water typically originates from groundwater sources that flow through limestone, chalk, or gypsum, which are rich in calcium and magnesium minerals.
Aquifers: Water from underground aquifers often contains high levels of these minerals, contributing to water hardness.
Municipal Water Supply:
Local Water Treatment: Even municipal water supplies can have varying levels of hardness depending on the natural sources and the treatment processes used. Some municipal systems do not remove all the calcium and magnesium, resulting in hard water.
Private Wells:
Well Water: Homes that rely on private wells often have hard water because well water directly taps into groundwater, which can have high mineral content depending on the local geology.
Surface Water Sources:
Lakes and Rivers: In some regions, surface water from lakes and rivers can also contain dissolved minerals, though generally, groundwater sources are more likely to contribute to hard water issues.
By employing these methods, you can effectively mitigate the effects of hard water in your home, protecting your plumbing, appliances, and improving your overall water quality and personal comfort.
1. Water Softeners:
Water softeners are devices designed to reduce the hardness of water by removing minerals that cause hardness, primarily calcium and magnesium. The most common type of water softener uses an ion exchange process to achieve this. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how they work:
Ion Exchange Systems: Traditional water softeners use ion exchange to replace calcium and magnesium ions with sodium or potassium ions, effectively softening the water.
Salt-Free Conditioners: These systems use various methods, such as template-assisted crystallization, to prevent minerals from forming scale, without adding sodium to the water.
2. Reverse Osmosis Systems:
Filtration: Reverse osmosis systems force water through a semipermeable membrane, removing a wide range of contaminants, including minerals that cause hardness. They are typically installed under the sink or as whole-house systems.
3. Whole-House Filtration Systems:
Combination Filters: Some whole-house systems combine different filtration methods to address various water quality issues, including hardness. They can include sediment filters, carbon filters, and softening components.
4. Regular Maintenance:
Descaling Appliances: Regularly descale appliances like kettles, coffee makers, and dishwashers using vinegar or commercial descaling solutions to remove mineral buildup.
Cleaning Fixtures: Clean and maintain plumbing fixtures and showerheads to remove scale and prevent clogging.
5. Choose Compatible Products:
Detergents and Soaps: Use detergents and soaps designed for hard water, which are formulated to work better in the presence of minerals.
Rinse Aids: Use rinse aids in dishwashers to prevent spotting and mineral buildup on dishes and glassware.

How Water Softeners Work :
Water softeners are devices designed to reduce the hardness of water by removing minerals that cause hardness, primarily calcium and magnesium. The most common type of water softener uses an ion exchange process to achieve this. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how they work:
Resin Beads: Water softeners contain a tank filled with small resin beads that are negatively charged and coated with sodium or potassium ions.
Ion Exchange: As hard water passes through the resin tank, the positively charged calcium and magnesium ions are attracted to the negatively charged resin beads. The resin beads exchange the sodium or potassium ions with the calcium and magnesium ions, effectively removing the hardness minerals from the water.
Softened Water: The water that exits the softener is now free of hardness minerals and contains the sodium or potassium ions instead.

Our water quality experts will show you exactly what contaminants are in your water with independent testing.
Combat Dry and Cracked Skin: The Impact of Hard Water and Soap over Usage.
Discover How Many Particles Your Family's Drinking Water Contains.
Reveal Your Water's Particles and How we can Eliminate those Toxins.
Reveals the difference between their water and filtered water - Consequence of doing NOTHING!
Identifying Toxins in Your Water: Empowering You to Choose What Stays or Goes.
Click the button below and complete our quick survey to get started with our water specialist!
Click to Schedule-Free Water Test-